科学足迹出版社供稿:科学足迹出版社(SFP)
期刊: Scientifc Reports
期刊: 科学报告
题目: Study of wave propagation in discontinuous and heterogeneous media with the dynamic lattice method
题目: 基于动态晶格法的波在不连续非均匀介质中的传播研究
作者: Amir S. Sattari, Zarghaam H. Rizvi, Hendrawan D. B.Aji & Frank Wuttke
摘要: The development of a new dynamic lattice element method (dynamicLEM) as well as its application in the simulation of the propagation of body waves in discontinuous and heterogeneous media is the focus of this research paper. The conventional static lattice models are efcient numerical methods to simulate crack initiation and propagation in cemented geomaterials. The advantages of the LEM and the developed dynamic solution, such as simulation of arbitrary crack initiation and propagation, illustration and simulation of existing inherent material heterogeneity as well as stress redistribution upon crack opening, opens a new engineering feld and tool for material analysis. To realize the time dependency of the dynamic LEM, the equation of motion of forced vibration is solved while using the Newmark-β method and implementing the non-linear Newton–Raphson Jacobian method. The method validation is done according to the results of a boundary element method (BEM) in the plane P-SV-wave propagation within a plane strain domain. Further tests comparing the generated wave types, simulation and study of crack discontinuities as well as inherent heterogeneities in the geomaterials are conducted to illustrate the accurate applicability of the new dynamic lattice method. The results indicate that with increasing heterogeneity within the material, the wave feld becomes signifcantly scattered and further analysis of wave felds according to the wavelength/heterogeneity ratio become indispensable. Therefore, in a heterogeneous medium, the application of continuum methods in relation to structural health monitoring should be precisely investigated and improved. The developed dynamic lattice element method is an ideal simulation tool to consider particle scale irregularities, crack distributions and inherent material heterogeneities and can be easily implemented in various engineering applications.
摘要: 本文主要研究新的动态晶格法(dynamicLEM)的发展,以及其研究体波在不连续非均质介质传播中的应用。传统的静态晶格模型可有效的对胶结土工程中裂纹产生和生长进行数字模拟。目前,已经有一些晶格法的动态解决方案,例如任意裂纹的产生和生长模拟、现有材料固有非均质性展示和模拟、和材料分析工具。这些动态解决方案和晶格法的优势相辅相成,可开创材料分析的新工程领域和工具。为了达到dynamicLEM的动态时间要求,在使用纽马克-β法和牛顿-拉弗森雅可比方法时,我们同时求解受迫振动运动方程。该方法的验证系由平面应变域内运用边界元法(BEM)对平面P-SV波传播进行测算完成。随后,我们进行了一系列进一步测试,致力于对比生成的波、岩土材料固有的非均质性不同时的情况,并模拟和研究裂纹不连续性,以展示新动态晶格方法的准确适用性。结果表明,随着材料内异质性的增加,波场出现明显散射,根据波场/非均质比对波场进一步分析变得不可或缺。因此,在异质介质中,我们应对采用连续体方法去做结构健康监测的应用进行精确调查和改进。我们所开发的动态晶格方法是考虑颗粒尺寸不规则形,裂纹分布和固有材料非均质性的理想模拟工具,且该方法可以在各类工程中轻松实现。
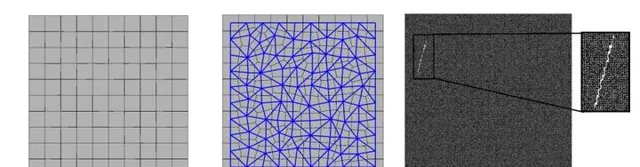
Figure 1. Discretization of a 2D domain: (a) generated Voronoi cells, when αf = 0.01, (b) generated lattice elements using Delaunay Triangulation (blue lines), when αf = 0.5, and (c) generated random crack, when αf = 0.5 and mesh size is 200 by 200.
图 1. 2D域的离散化: (a) αf = 0.01时生成的沃罗诺伊网格, (b) 当αf = 0.5时,使用狄洛尼三角剖分得到的晶格,和(c) 当αf = 0.5 网格尺寸为200*200时随机生成的裂纹。

Figure 2. Generated heterogeneous granular domain: (a) uniform aggregate-bond distribution, D = 2 ∼ 4 mm, (b) non-uniform aggregate-bond distribution, D = 1 ∼ 10 mm, and (c) arbitrarily distributed heterogeneity, when αf = 0.5 and mesh size is 600 by 600.
图 2.生成的异质颗粒域: (a) 均匀聚集键分布, D = 2 ∼ 4 mm, (b) 非均匀聚集键分布, D = 1 ∼ 10 mm, 和 (c) 当αf = 0.5、网格尺寸为600*600时的任意分布的非均质
文章来源:
https://www. nature.com/articles/s41 598-022-10381-y
以上中文翻译为译者个人对于文章的概略理解,论文传递的准确信息请参照英文原文。