科學足跡出版社供稿:科學足跡出版社(SFP)
期刊: Scientifc Reports
期刊: 科學報告
題目: Study of wave propagation in discontinuous and heterogeneous media with the dynamic lattice method
題目: 基於動態晶格法的波在不連續非均勻介質中的傳播研究
作者: Amir S. Sattari, Zarghaam H. Rizvi, Hendrawan D. B.Aji & Frank Wuttke
摘要: The development of a new dynamic lattice element method (dynamicLEM) as well as its application in the simulation of the propagation of body waves in discontinuous and heterogeneous media is the focus of this research paper. The conventional static lattice models are efcient numerical methods to simulate crack initiation and propagation in cemented geomaterials. The advantages of the LEM and the developed dynamic solution, such as simulation of arbitrary crack initiation and propagation, illustration and simulation of existing inherent material heterogeneity as well as stress redistribution upon crack opening, opens a new engineering feld and tool for material analysis. To realize the time dependency of the dynamic LEM, the equation of motion of forced vibration is solved while using the Newmark-β method and implementing the non-linear Newton–Raphson Jacobian method. The method validation is done according to the results of a boundary element method (BEM) in the plane P-SV-wave propagation within a plane strain domain. Further tests comparing the generated wave types, simulation and study of crack discontinuities as well as inherent heterogeneities in the geomaterials are conducted to illustrate the accurate applicability of the new dynamic lattice method. The results indicate that with increasing heterogeneity within the material, the wave feld becomes signifcantly scattered and further analysis of wave felds according to the wavelength/heterogeneity ratio become indispensable. Therefore, in a heterogeneous medium, the application of continuum methods in relation to structural health monitoring should be precisely investigated and improved. The developed dynamic lattice element method is an ideal simulation tool to consider particle scale irregularities, crack distributions and inherent material heterogeneities and can be easily implemented in various engineering applications.
摘要: 本文主要研究新的動態晶格法(dynamicLEM)的發展,以及其研究體波在不連續非均質介質傳播中的套用。傳統的靜態晶格模型可有效的對膠結土工程中裂紋產生和生長進行數位模擬。目前,已經有一些晶格法的動態解決方案,例如任意裂紋的產生和生長模擬、現有材料固有非均質性展示和模擬、和材料分析工具。這些動態解決方案和晶格法的優勢相輔相成,可開創材料分析的新工程領域和工具。為了達到dynamicLEM的動態時間要求,在使用紐馬克-β法和牛頓-拉弗森亞可比方法時,我們同時求解受迫振動運動方程式。該方法的驗證系由平面應變域內運用邊界元法(BEM)對平面P-SV波傳播進行測算完成。隨後,我們進行了一系列進一步測試,致力於對比生成的波、巖土材料固有的非均質性不同時的情況,並模擬和研究裂紋不連續性,以展示新動態晶格方法的準確適用性。結果表明,隨著材料內異質性的增加,波場出現明顯散射,根據波場/非均質比對波場進一步分析變得不可或缺。因此,在異質介質中,我們應對采用連續體方法去做結構健康監測的套用進行精確調查和改進。我們所開發的動態晶格方法是考慮顆粒尺寸不規則形,裂紋分布和固有材料非均質性的理想模擬工具,且該方法可以在各類工程中輕松實作。
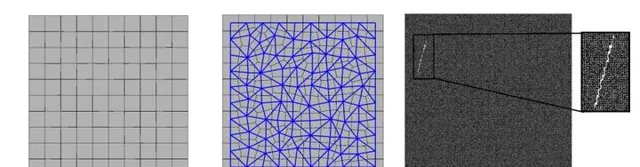
Figure 1. Discretization of a 2D domain: (a) generated Voronoi cells, when αf = 0.01, (b) generated lattice elements using Delaunay Triangulation (blue lines), when αf = 0.5, and (c) generated random crack, when αf = 0.5 and mesh size is 200 by 200.
圖 1. 2D域的離散化: (a) αf = 0.01時生成的沃羅諾伊網格, (b) 當αf = 0.5時,使用狄洛尼三角剖分得到的晶格,和(c) 當αf = 0.5 網格尺寸為200*200時隨機生成的裂紋。

Figure 2. Generated heterogeneous granular domain: (a) uniform aggregate-bond distribution, D = 2 ∼ 4 mm, (b) non-uniform aggregate-bond distribution, D = 1 ∼ 10 mm, and (c) arbitrarily distributed heterogeneity, when αf = 0.5 and mesh size is 600 by 600.
圖 2.生成的異質顆粒域: (a) 均勻聚集鍵分布, D = 2 ∼ 4 mm, (b) 非均勻聚集鍵分布, D = 1 ∼ 10 mm, 和 (c) 當αf = 0.5、網格尺寸為600*600時的任意分布的非均質
文章來源:
https://www. nature.com/articles/s41 598-022-10381-y
以上中文轉譯為譯者個人對於文章的概略理解,論文傳遞的準確資訊請參照英文原文。