關註風雲之聲
提升思維層次
導讀
實作碳中和的路徑是什麽?實作碳中和的技術突破方向是什麽?如何監測和計量碳排放?本文匯聚來自8個國家、52個單位的58位元學者(8位元院士),系統評述了碳中和技術及前景,為全球實作碳中和 提供支撐。

導語|Introduction
隨著化石燃料的大規模使用、森林砍伐和土地利用方式 的變更,人類活動導致大氣中的溫室瓦斯濃度不斷增加,引起全球氣候變暖。為應對日益嚴峻的氣候挑戰,力爭在本世紀中期實作 碳中和 是全球共同的使命。實作碳中和的 路徑 是什麽?實作碳中和的技術 突破方向 是什麽?如何 監測和計量 碳排放?本文匯聚來自8個國家、52個單位的58位元學者(8位元院士),系統評述了碳中和技術及前景,為全球實作碳中和提供支撐。
With the extensive use of fossil fuels, deforestation, and land-use change, anthropogenic activities have contributed to the ever-increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere, causing global climate change. In response to the worsening global climate change, achieving carbon (C) neutrality by the middle century is the most pressing task on the planet. What are the paths to C neutralization? What are the directions for technological breakthroughs to achieve C neutralization? How to monitor and measure C emissions? This review, prepared by 58 scientists from 8 countries and 52 research units, intends to provide insights into the innovative technologies that offer solutions achieving C neutrality and sustainable development.
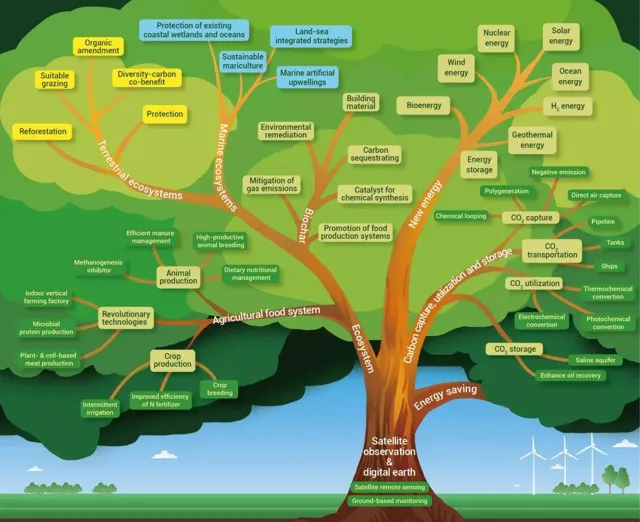
圖1 圖文摘要
Fig. 1 Graphical Abstract
1. 可再生能源技術
Technologies for renewable energy
對標碳中和,實作一次能源有序減量替代,需大力發展可再生能源 。可再生能源是一個完整的技術體系,不僅需要太陽能、風能、地熱能、海洋能等,更需要儲能技術 的配合,形成真正的新能源體系。核能與氫能具有清潔低碳、綠色環保等優點,是實作碳中和目標的重要技術;生物質能也是實作能源結構調整的重要支撐。本文總結了可再生能源大規模套用中的關鍵核心技術,以及這些關鍵核心技術對實作碳中和目標的影響,同時對這些技術未來的發展進行了展望(圖2)。
Achieving C neutrality requires replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources. Harnessing the power of solar, wind, geothermal, ocean, nuclear, and p energy may help secure global energy security without relying on fossil fuels. Bioenergy is also important in reshaping the energy supply and consumption systems. Technologies for these renewable energy sources and their future development are discussed (Fig. 2).
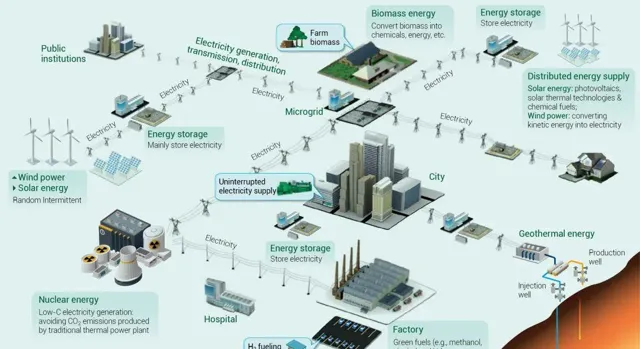
圖2 可再生能源技術
Fig. 2 Technologies for renewable energy
2. 增強全球生態系碳匯技術
Technologies for enhancing C sink in global ecosystems
為實作全球生態系碳中和,迫切需要減少農業食物源溫室瓦斯排放和提高生物圈的碳固持量 (圖3)。選育優良作物和家畜品種,農田精準灌溉、施肥與土壤增碳,最佳化家畜飼養和糞便管理,變革基於土地利用的動植食物生產等措施,以減少農業食物源溫室瓦斯排放;實施永續管理森林草地生態系 ,增強巖石風化作用和采用生物炭技術等措施提高陸地生態碳匯;透過保護濱海濕地與海洋生態系,實施永續海水養殖、人工湧升流和陸海一體化戰略,提升海洋生態系碳匯能力。
Global agricultural food systems are the major source of global anthropogenic GHG emissions, while terrestrial and marine ecosystems are the most important global C sinks (Fig. 3). To avoid disastrous climate change, global ecosystems need to be reformed to increase C sequestration, biomass production, and food supply while lowering GHG emissions.
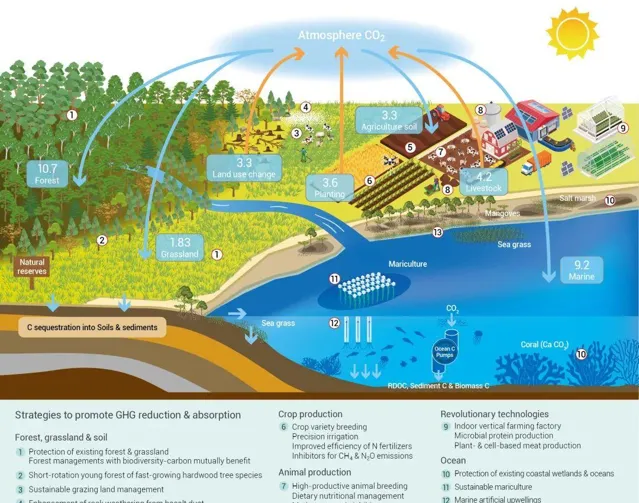
圖3 全球生態系溫室瓦斯流通量、減排和吸收策略
Fig. 3 Overview of global GHG budget and strategies to promote GHG reduction and sequestration in global ecosystems
3. 解決全球廢棄物碳足跡問題
Tackling the C footprint of global waste
作為減少全球廢棄物碳足跡的有效策略, 將固體廢棄物轉化為生物炭,能夠減少溫室瓦斯排放,實作碳封存,有利於促進迴圈經濟發展 。大量有機廢棄物 ,如植物殘體、牲畜糞便、廚余垃圾、工業生物垃圾、動物屍體等,都可制備生物炭。生物質炭可用於土壤改良、環境修復、化學品生產、建築材料和飼料配方(圖4)。
As an effective strategy to reduce the C footprint of global waste, thermochemical conversion of solid waste into biochar can bring multifunctional benefits to the circular economy in addition to climate change mitigation and C sequestration. A plethora of organic resources, such as crop residues, forest residues, livestock manure, food wastes, industrial biowastes, municipal biowastes, animal carcasses, are feedstocks that can be used to produce biochar for different purposes. Biochar is used in a variety of applications, including soil amendment, delivery of agrochemicals and microbes, environmental remediation, catalyst production, building material manufacturing, and feed formulation (Fig. 4).

圖4 零廢棄生物炭作為永續發展的碳中和工具
Fig. 4 Zero waste biochar as a C-neutral tool for sustainable development
4. 碳捕集 、利用和儲存的技術
Technologies for C capture, utilization, and storage
CCUS是捕集、利用和儲存CO2的技術,對實作碳中和至關重要。 CCUS需要技術創新以實作低成本和近零能耗捕集,同時實作碳封存與地下資源開采協同和風險管理技術 。未來的突破方向:化學鏈燃燒、多聯產、化石能源和可再生能源互補捕集CO2等技術。CO2轉化為燃料或者化工品也是碳減排的重要途徑(圖5)。
CCUS, technologies for carbon capture, utilization, and storage, are critical to achieving C neutrality (Fig. 5). CCUS technologies need innovations, targeting CO2 recovery with low energy or even zero energy penalty, and aiming collaborative optimization of CO2 storage and resource recovery and risk management. Chemicals-power polygeneration and chemical looping combustion with CO2 capture have the potentials to realize low-cost CO2 capture. Fossil fuels combined with renewable energy for CO2 capture, the complementary energy systems, may play an important role for future CCUS. The conversion of CO2 into fuels and chemicals is a promising direction for C reduction.

圖5 工業體系二氧化碳捕集技術發展的路線圖
Fig. 5 The roadmap for CO2 capture technology development in the industry
5. 衛星對地觀測與數位地球 技術
C neutrality based on satellite observations and digital earth
衛星對地觀測和數位地球技術是空天地一體監測碳迴圈的重要手段 ,能為碳中和研究提供高時空分辨率的基礎觀測數據和分析工具。碳衛星 、多光譜衛星為監測溫室瓦斯濃度提供數據支撐;數位地球技術綜合全球植被、大氣、氣候數據,為自然生態系碳收支提供時空分析與視覺化展示。
Satellite observation and digital earth technology are important parts of monitoring C emissions and establishing an air-space-ground integrated observation system for the C cycle. They can provide basic observation and analysis data with a high temporal and spatial resolution for C neutralization research. C satellite and multispectral satellites can provide data support for monitoring the concentration of greenhouse gases; digital earth technology can integrate global vegetation , atmosphere, and climate data to provide temporal and spatial analysis of the C budget of natural ecosystems.
總結與展望 | Conclusions & perspectives
世界正朝著碳中和邁進,未來需構建以清潔能源為主體的新型電力系統,實作一次能源有序減量替代和可再生能源的大規模套用;統籌生態系保護和固碳功能,推進基於土地利用與食物生產變革,提高陸海一體生態碳匯;最佳化生物炭生產和生命周期過程,制定標準推進低碳產業發展;利用多聯產技術、化學鏈燃燒技術、化石燃料與可再生能源互補技術,解決CCUS技術推廣高能耗高成本障礙;發展新型衛星,全面監測溫室瓦斯排放和陸海碳匯,星地協同增強碳收支核算能力。全球須通力合作、技術共享,以早日實作碳中和與永續發展。
As the world races towards C neutrality, it is critical to revise current global C fluxes. To meet the climate change mitigation goals by the middle century, all people including investors, researchers, policy makers and consumers must work together:
(1) To realize orderly reduction and replacement of fossil fuel energy sources with renewable energy sources , we need to vigorously develop energy storage systems to address the intermittency of renewable energy sources. (2) To coordinate ecosystem protection and carbon sequestration, we need to push forward reform of crop-livestock production systems based on land use and improving ecological carbon sink. (3) To integrate ecological strategies optimizing biochar production, life cycle analysis, and formulate standards to advance the development of green and low-carbon industries. (4) To adopt breakthrough CCUS technologies including polygeneration, chemical looping combustion, and fossil fuels combined with renewable energy for CO2 capture, to overcome the high energy consumption and high costs. (5) To develop new satellites to comprehensively and timely monitor GHG emissions, and to expand the ability to calculate C budgets through joint observation from space and the ground.

掃二維碼|檢視原文
原文連結:https://www. cell.com/the-innovation /fulltext/S2666-6758(21) 00105-3
本文內容來自 Cell Press 合作期刊 The Innovation 第二卷第四期以Review發表的「Technologies and perspectives for achieving carbon neutrality」 (投稿: 2021-09-20;接收: 2021-10-27;線上刊出: 2021-10-29)。
DOI : https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn. 2021.100180
參照格式 :Wang F., Harindintwali J., Yuan Z., et al. (2021). Technologies and perspectives for achieving carbon neutrality . The Innovation . 2(4),100180.
謹以此文致敬中國科學院青年創新促進會成立十周年!
The study is dedicated to the 10th anniversary of Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
第一兼通訊作者:

王 芳 ,中國科學院南京土壤研究所 研究員 ,德國洪堡資深學者;從事土壤汙染修復研究,發表論文160篇;擔任國際原子能總署顧問、Sci Total Environ副主編。
並列第一作者:

袁治章 ,中國科學院大連化學物理研究所 研究員 ,鋅基液流電池 技術研究組組長;從事鋅基液流電池材料的研發、電堆規模放大理論及工程技術研究。

王 敏 ,中國科學院副熱帶農業生態研究所 研究員 ,國家自然科學基金優秀青年基金獲得者,中科院青促會優秀會員,從事畜牧業溫室瓦斯排放、胃腸道氫代謝與甲烷減排調控研究。

李 勝 ,中國科學院工程熱物理研究所 研究員 ,國家自然科學基金 優秀青年基金獲得者,中科院青促會優秀會員;長期從事能源系統整合、煤氣化和CO2捕集方面的研究工作。

黃 磊 ,中國科學院空天資訊創新研究院 副研究員 ,中科院青促會會員。負責利用地球大數據支持SDG13氣候行動工作,研究興趣包括冰川變化和溫室瓦斯遙感。
並列通訊作者:

李先鋒 ,中國科學院大連化學物理研究所 副所長 ,國家傑出青年科學基金 獲得者,從事電化學儲能技術開發工作;榮獲國家技術發明二等獎,發表SCI論文250余篇,引被1萬余次,授權發明專利150余項;擔任Chinese Chem Lett副主編。

焦念誌 , 中國科學院院士 ,開發中國家科學院院士 ;從事海洋生態過程與資源環境效應研究,獲國家自然科學二等獎;發表論文200余篇,主編Science增刊,連續多年評為高被引學者 ;出版專著3部;擔任【中國科學:地球科學 】副主編。

朱永官 , 中國科學院院士 ,開發中國家科學院院士;從事環境土壤學和環境生物學研究,主持國家自然科學基金委 重大計畫,獲得國家自然科學二等獎和開發中國家科學院農業科學獎。在Science、Nature等發表論文300余篇,被引1萬余次;擔任Environ Int主編。

金紅光 , 中國科學院院士 ,中國科學院工程熱物理研究所研究員;從事總能系統、分布式能源、太陽能熱利用和碳捕集等研究。曾獲國家自然學科二等獎、何梁何利獎 等;發表論文200余篇,授權發明專利30余項。

James M Tiedje , 美國科學院院士 ,密西根州立大學傑出教授,美國科學促進會、微生物學會、土壤學會和農學會Fellow,現代微生物生態學之父,建立了國際微生物生態學學會,獲聯合國教科文組織Finlay獎,發表論文700多篇,被引11.3萬余次,H指數168。

陳鏡明 , 加拿大皇家科學院院士 ,多倫多大學教授,加拿大首席科學家;從事植被遙感、生態和氣候變遷研究,發表SCI論文400余篇,被引3.3萬余次,H指數89;現任Remote Sens Environ主編、中國科技部全球變化重點研發計畫 專家組成員。
主要作者:

陳溫福 , 中國工程院院士 ,沈陽農業大學水稻研究所所長;從事生物質炭 的生產與套用研究,獲國家科技進步二等獎、全國模範教師、全國「五一」勞動獎章和全國勞動模範等;擔任Biochar主編,發表論文200余篇,出版專著4部,授權發明專利9項。

Johannes Lehmann , 德國科學院院士 ,康內爾大學 傑出教授,國際土壤碳網路指導小組成員,聯合國防治荒漠化公約評估小組成員,從事生物地理化學、土壤固碳和生物炭系統和熱帶永續農業方向研究;在Science、Nature等發表論文300多篇,被引6.3萬余次。

Andreas Schaeffer , 德國科學院院士 ,阿亨工業大學 環境研究所所長,科技部高端外國專家,從事汙染物多界面化學遷移與代謝,汙染修復和風險評估等研究,發表論文200多篇,被引6900余次,H指數40。
擴充套件閱讀:
氣候變遷的自然科學基礎:IPCC報告的新認知 | TheInnovation創新
背景簡介: 本文2021年11月15日發表於微信公眾號 TheInnovation創新 (The Innovation | 碳中和技術與前景The Innovation | 碳中和技術與前景),風雲之聲獲授權轉載。責任編輯:陳昕悅











