一、字元裝置基礎
字元裝置:是指只能一個字節一個字節進行讀寫操作的裝置,不能隨機讀取裝置中的某一數據、讀取數據要按照先後數據。字元裝置是面向流的裝置,常見的字元裝置有滑鼠、鍵盤、串口、控制台和LED等。
一般每個字元裝置或者塊裝置都會在/dev目錄(可以是任意目錄,這樣是為了統一)下對應一個裝置檔。linux使用者層程式透過裝置檔來使用驅動程式操作字元裝置或塊裝置。
二、字元裝置驅動與使用者空間存取該裝置的程式三者之間的關系
字元裝置是3大類裝置(字元裝置、塊裝置、網路裝置)中較簡單的一類裝置、其驅動程式中完成的主要工作是初始化、添加和刪除 struct cdev 結構體,申請和釋放裝置號,以及填充 struct file_operations 結構體中斷的操作函式,實作 struct file_operations 結構體中的read()、write()和ioctl()等函式是驅動設計的主體工作。
如圖,在Linux內核程式碼中:
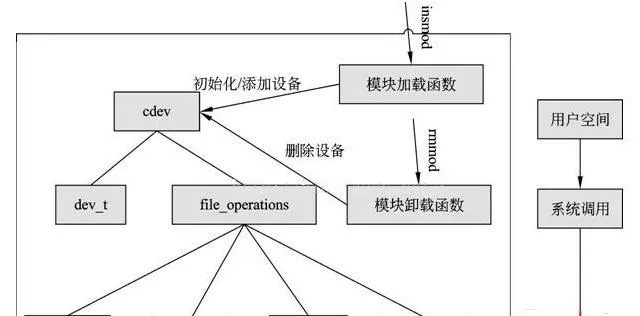
三、字元裝置模型
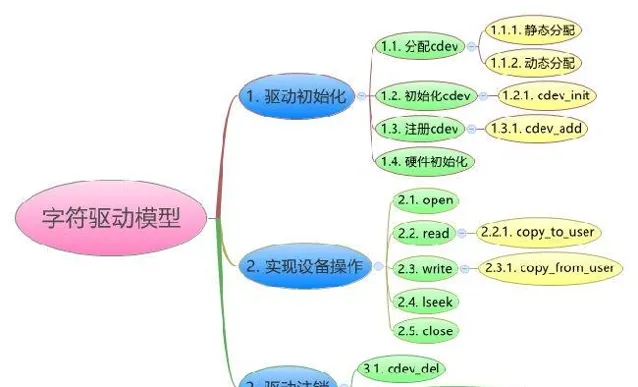
1、Linux內核中,使用 struct cdev 來描述一個字元裝置
<include/linux/cdev.h>
struct cdev {
struct kobject kobj; //內嵌的內核物件.
struct module *owner; //該字元裝置所在的內核模組(所有者)的物件指標,一般為THIS_MODULE主要用於模組計數
const struct file_operations *ops; //該結構描述了字元裝置所能實作的操作集(開啟、關閉、讀/寫、...),是極為關鍵的一個結構體
struct list_head list; //用來將已經向內核註冊的所有字元裝置形成連結串列
dev_t dev; //字元裝置的裝置號,由主裝置號和次裝置號構成(如果是一次申請多個裝置號,此裝置號為第一個)
unsigned int count; //隸屬於同一主裝置號的次裝置號的個數
...
};
對於struct cdev內核提供了一些操作介面:
表頭檔linux/cdev.h
動態申請(構造)cdev記憶體(裝置物件)
struct cdev *cdev_alloc(void);
/* 返回值:
成功 cdev 物件首地址
失敗:NULL */
初始化cdev的成員,並建立cdev和file_operations之間關聯起來
void cdev_init(struct cdev *p, const struct file_operations *p);
/* 參數:
struct cdev *p - 被初始化的 cdev物件
const struct file_operations *fops - 字元裝置操作方法集 */
註冊cdev裝置物件(添加到系統字元裝置列表中)
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p, dev_t dev, unsigned count);
/* 參數:
struct cdev *p - 被註冊的cdev物件
dev_t dev - 裝置的第一個裝置號
unsigned - 這個裝置連續的次裝置號數量
返回值:
成功:0
失敗:負數(絕對值是錯誤碼)*/
將cdev物件從系統中移除(登出 )
void cdev_del(struct cdev *p); /*參數: struct cdev *p - 要移除的cdev物件 */
釋放cdev記憶體
void cdev_put(struct cdev *p); /*參數: struct cdev *p - 要移除的cdev物件 */
2、裝置號申請/釋放
一個字元裝置或塊裝置都有一個主裝置號和一個次裝置號。主裝置號用來標識與裝置檔相連的驅動程式,用來反映裝置型別。次裝置號被驅動程式用來辨別操作的是哪個裝置,用來區分同型別的裝置。
linux內核中,裝置號用dev_t來描述:
typedef u_long dev_t; // 在32位元機中是4個字節,高12位元表示主裝置號,低20位表示次裝置號。
內核也為我們提供了幾個方便操作的宏實作dev_t:
#define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS)) // 從裝置號中提取主裝置號
#define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK)) // 從裝置號中提取次裝置號
#define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi))</span> // 將主、次裝置號拼湊為裝置號
/* 只是拼湊裝置號,並未註冊到系統中,若要使用需要競態申請 */
表頭檔 linux/fs.h
a - 靜態申請裝置號
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name);
/* 參數:
dev_t from - 要申請的裝置號(起始)
unsigned count - 要申請的裝置號數量
const char *name - 裝置名
返回值:
成功:0
失敗:負數(絕對值是錯誤碼)*/
b - 動態分配裝置號
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name);
/* 參數:
dev_t *dev - 用於保存分配到的第一個裝置號(起始)
unsigned baseminor - 起始次裝置號
unsigned count - 要分配裝置號的數量
const char *name - 裝置名
返回值:
成功:0
失敗:負數(絕對值是錯誤碼)*/
c - 釋放裝置號
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count);
/* 參數:
dev_t from - 要釋放的第一個裝置號(起始)
unsigned count - 要釋放的次裝置號數量 */
d、建立裝置檔:
利用cat /proc/devices檢視申請到的裝置名,裝置號。
- 使用mknod手工建立:mknod filename type major minor
- 自動建立裝置節點:利用udev(mdev)來實作裝置檔的自動建立,首先應保證支持udev(mdev),由busybox配置。在驅動初始化程式碼裏呼叫 class_create為該裝置建立一個 class,再為每個裝置呼叫device_create建立對應的裝置。
詳細解析見:
Linux裝置檔自動生成
3、struct cdev 中的 file_operations *fops成員
Linux下一切皆是「檔」,字元裝置也是這樣,file_operations結構體中的成員函式是字元裝置程式設計的主題內容,這些函式實際會在使用者層程式進行Linux的open()、close()、write()、read()等系統呼叫時最終被呼叫。
標準化:如果做到極致,套用層僅僅需要一套系統呼叫介面函式。
"檔"的操作介面結構:
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner; /* 模組擁有者,一般為 THIS——MODULE */
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); /* 從裝置中讀取數據,成功時返回讀取的字節數,出錯返回負值(絕對值是錯誤碼) */
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); /* 向裝置發送數據,成功時該函式返回寫入字節數。若為被實作,使用者調層用write()時系統將返回 -EINVAL*/
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); /* 將裝置記憶體對映內核空間行程記憶體中,若未實作,使用者層呼叫 mmap()系統將返回 -ENODEV */
long (*unlocked_ioctl)(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); /* 提供裝置相關控制命令(讀寫裝置參數、狀態,控制裝置進行讀寫...)的實作,當呼叫成功時返回一個非負值 */
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); /* 開啟裝置 */
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); /* 關閉裝置 */
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id); /* 重新整理裝置 */
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); /* 用來修改檔讀寫位置,並將新位置返回,出錯時返回一個負值 */
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int); /* 通知裝置 FASYNC 標誌發生變化 */
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); /* POLL機制,用於詢問裝置是否可以被非阻塞地立即讀寫。當詢問的條件未被觸發時,使用者空間進行select()和poll()系統呼叫將引起行程阻塞 */
...
};
四、簡單字元裝置例項
cdev_module.c
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <asm/current.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
static int major = 0; static int minor = 0; const int count = 3; #define DEVNAME "demo" static struct cdev *demop = NULL; //開啟裝置 static int demo_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { //get command and pid printk(KERN_INFO "(%s:pid=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", current->comm, current->pid, __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); //get major and minor from inode printk(KERN_INFO "(major=%d, minor=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", imajor(inode), iminor(inode), __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); return 0; } //關閉裝置 static int demo_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { //get command and pid printk(KERN_INFO "(%s:pid=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", current->comm, current->pid, __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); //get major and minor from inode printk(KERN_INFO "(major=%d, minor=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", imajor(inode), iminor(inode), __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); return 0; } //讀裝置static ssize_t demo_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) { struct inode *inode = filp->f_path.dentry->d_inode; //get command and pid printk(KERN_INFO "(%s:pid=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", current->comm, current->pid, __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); //get major and minor from inode printk(KERN_INFO "(major=%d, minor=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", imajor(inode), iminor(inode), __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); return 0; } //寫裝置 static ssize_t demo_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) { struct inode *inode = filp->f_path.dentry->d_inode; //get command and pid printk(KERN_INFO "(%s:pid=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", current->comm, current->pid, __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); //get major and minor from inode printk(KERN_INFO "(major=%d, minor=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", imajor(inode), iminor(inode), __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); return 0; } //操作方法集 static struct file_operations fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = demo_open, .release= demo_release, .read = demo_read, .write = demo_write, }; //cdev裝置模組初始化 static int __init demo_init(void) { dev_t devnum; int ret; //get command and pid printk(KERN_INFO "(%s:pid=%d), %s : %s : %d\n", current->comm, current->pid, __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__); //1. alloc cdev obj demop = cdev_alloc(); if(NULL == demop) { return -ENOMEM; }
//2. init cdev obj
cdev_init(demop, &fops); ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devnum, minor, count, DEVNAME);
if(ret){
goto ERR_STEP;
}
major = MAJOR(devnum);
//3. register cdev obj
ret = cdev_add(demop, devnum, count);
if(ret){
goto ERR_STEP1;
}
//get command and pid
printk(KERN_INFO "(%s:pid=%d), %s : %s : %d - ok.\n", current->comm, current->pid, __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
ERR_STEP1:
unregister_chrdev_region(devnum, count);
ERR_STEP:
cdev_del(demop);
//get command and pid
printk(KERN_INFO "(%s:pid=%d), %s : %s : %d - fail.\n", current->comm, current->pid, __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__);
return ret;
}
static void __exit demo_exit(void)
{
//get command and pid
printk(KERN_INFO "(%s:pid=%d), %s : %s : %d - leave.\n", current->comm, current->pid, __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major, minor), count);
cdev_del(demop);
}
module_init(demo_init);
module_exit(demo_exit);
test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int num, char *arg[])
{
if(2 != num){
printf("Usage: %s /dev/devfile\n", arg[0]);
return -1;
}
int fd = open(arg[1], O_RDWR);
if(0 > fd){
perror("open");
return -1;
}
getchar();
int ret = read(fd, 0x321, 0);
printf("read: ret = %d.\n", ret);
getchar();
ret = write(fd, 0x123, 0);
printf("write: ret = %d.\n", ret);
getchar();
close(fd);
return 0;
}
Makefile
1ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
2obj-m = demo.o
3
| 1234567891011 | ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) obj-m = demo.oelse KERNELDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build PWD := $(shell pwd)modules: $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modulesendif clean: rm -rf .tmp_versions Module.symvers modules.order .tmp_versions .*.cmd *.o *.ko *.mod.c |
4KERNELDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
5PWD := $(shell pwd)
6modules:
7$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
8endif
9
10
| 1234567891011 | ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) obj-m = demo.oelse KERNELDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build PWD := $(shell pwd)modules: $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modulesendif clean: rm -rf .tmp_versions Module.symvers modules.order .tmp_versions .*.cmd *.o *.ko *.mod.c |
11
| 1234567891011 | ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) obj-m = demo.oelse KERNELDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build PWD := $(shell pwd)modules: $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modulesendif clean: rm -rf .tmp_versions Module.symvers modules.order .tmp_versions .*.cmd *.o *.ko *.mod.c |
編譯成功後,使用 insmod 命令載入:
然後用cat /proc/devices 檢視,會發現裝置號已經申請成功












